A Practical Guide to HS Code Dubai Customs
Master the hs code dubai customs 12-digit system. Our guide helps UAE finance managers avoid costly errors and ensure seamless import compliance.

Posted by
Related Reading
Your Guide to the HS Code UAE System for Tax and Customs
Master the HS Code UAE system. Learn to find and use the correct 12-digit codes for customs, VAT, and FTA e-invoicing compliance.
Read →
Unlocking HS Code Dubai: Your Guide to Accurate Classification & Compliance
Master hs code dubai with practical steps for accurate classification, customs compliance, and UAE e-invoicing readiness.
Read →
Debit Note and Credit Note: A Practical Guide for UAE E-Invoicing
Master the debit note and credit note for UAE VAT and e-invoicing. Learn their purpose, format, and how to ensure FTA compliance with PINT AE standards.
Read →
At its core, an HS code is the universal language of international trade. It’s a standardised numbering system that Dubai Customs, and virtually every other customs authority worldwide, uses to identify and classify products crossing their borders.
For any business importing to or exporting from the UAE, getting this code right isn't optional—it's mandatory. This single code is the key that determines everything from customs duties and VAT to whether your goods are subject to special controls or inspections.
The New Era of UAE Customs Compliance
Recently, Dubai made a significant shift, moving from the standard 8-digit Harmonized System (HS) code to a more detailed 12-digit system. This isn’t just a minor administrative tweak; it's a fundamental change that redefines customs compliance for every single import and export operation.
For finance managers and accountants, this transition introduces a new layer of complexity. It directly impacts duty calculations, VAT reporting, and even the overall efficiency of your supply chain. This guide is here to help you navigate the new 12-digit HS code system, ensuring your customs declarations are spot-on, fully compliant, and free from expensive mistakes.

Getting to grips with this Dubai Customs update is more than just a box-ticking exercise; it's a strategic imperative. A single wrong digit can trigger a cascade of financial penalties and operational logjams, disrupting your business and putting a strain on your partnerships.
Why This Change Matters to Your Business
So, why the extra four digits? The move to a 12-digit system allows for an incredible level of detail and precision in product classification. While this granularity helps authorities manage trade flows more effectively, it puts the onus on businesses to be far more accurate.
Here’s a breakdown of what’s at stake:
- Financial Accuracy: The HS code is directly tied to the customs duty rate. A misclassification could easily lead to overpaying duties—or worse, underpaying them and facing hefty fines down the line.
- VAT Reporting: Import VAT is calculated on the value of your goods, which is established during the customs declaration. An incorrect HS code can throw off your VAT calculations, creating compliance headaches with the Federal Tax Authority (FTA).
- Operational Efficiency: Shipments with incorrect or questionable HS codes are prime targets for inspection. This can mean significant delays at the port, leading to frustrated customers and unplanned demurrage and storage charges.
As the UAE moves towards broader mandates like UAE e-invoicing, having clean, accurate foundational data is more important than ever. Your HS codes are a critical part of that foundation. Platforms like Tadqiq are designed to help businesses manage their tax and compliance workflows, and accurate customs data is a non-negotiable piece of that puzzle.
In the following sections, we’ll dive into the official tools, unpack the new tariff structure, and highlight the deadlines you simply can't afford to miss.
Cracking the Code: What's Inside the New 12-Digit HS Code?
The UAE's move to a 12-digit Integrated Customs Tariff isn't just a minor tweak; it's a major overhaul in how Dubai Customs sees and manages the goods flowing through our borders. For anyone in finance or logistics, getting your head around the structure of this code is the first, most critical step. It’s what stands between smooth operations and costly, frustrating delays.
Think of this 12-digit number as a detailed biography for your product. Every section tells a part of its story, starting with its broad international family and ending with its very specific identity right here in the UAE. This level of detail is precisely why Dubai Customs made the change—it gives them a crystal-clear picture of what's coming in and going out.
From a Global Blueprint to a Local Fingerprint
The beauty of the HS code Dubai Customs uses is its hierarchical structure. It starts broad and gets progressively more specific, like zooming in on a map. The first few digits are universal, spoken by customs authorities from Shanghai to San Francisco. The last few, however, are unique to our region and our country.
Let's break it down to see how it works:
-
Digits 1-6 (The Global Handshake): These are the original Harmonized System digits, managed by the World Customs Organization (WCO). They're the international standard, ensuring that a "smartphone" is classified similarly whether you're shipping it to Germany or Brazil. It’s the common language of global trade.
-
Digits 7-8 (The GCC Connection): The next two digits bring things closer to home. They are specific to the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC), creating a unified classification system for member states like Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, and Oman. This layer is all about simplifying trade within our immediate region.
-
Digits 9-12 (The UAE's National ID): This is where the real change happens. These final four digits are the UAE's own subclassifications. They allow Dubai Customs to identify products with pinpoint accuracy, which is essential for applying specific duties, excise taxes, or even prohibitions and restrictions.
This leap from an 8-digit to a 12-digit system is a game-changer. It’s not just about adding more numbers. It's about fundamentally reshaping how goods are categorised and controlled, directly impacting everything from duty calculations to how your shipment is flagged for inspection.
To really understand the new 12-digit UAE HS code, it's helpful to see its structure laid out. Each part of the code plays a distinct role, building a detailed profile of the product for customs purposes.
Anatomy of the New 12-Digit UAE HS Code
| Digit Positions | Level of Classification | Governing Body | Purpose and Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1-2 (Chapter) | Broadest Category | World Customs Organization (WCO) | 09: Coffee, Tea, Maté and Spices |
| 3-4 (Heading) | Specific Product Group | World Customs Organization (WCO) | 0901: Coffee, whether or not roasted or decaffeinated |
| 5-6 (Subheading) | Detailed Product Type | World Customs Organization (WCO) | 0901.11: Coffee, not roasted, not decaffeinated |
| 7-8 (Regional) | GCC-Specific Tariff | GCC Customs Union | 0901.11.10: Arabian coffee |
| 9-12 (National) | UAE-Specific Tariff | UAE Federal Customs Authority | 0901.11.10.0010: Certified organic Arabian coffee beans |
This breakdown shows how the code moves from a general category like "Coffee" all the way down to a very specific type, like "Certified organic Arabian coffee beans," with each layer adding a crucial piece of information for Dubai Customs.
Why This New Level of Detail Matters
This isn't a small adjustment. A recent analysis from PwC highlighted that the number of individual tariff lines in the UAE is jumping from roughly 7,800 under the old 8-digit system to over 13,400 with the new 12-digit codes. That’s a staggering increase of more than 70% in classification detail. For a deeper dive, the PwC report on the UAE's 12-digit tariff implementation is well worth a read.
For finance teams, the implications are immediate. Every single product in your inventory or ERP system now needs to be mapped to one of these highly specific new codes. What used to be a single 8-digit code for "marine mammals" might now be split into several 12-digit codes for "live whales," "live dolphins," and "live seals"—each potentially having different rules or duties.
Getting this 12-digit code right is everything. It's the number that determines the customs duty you pay, which in turn is the foundation for calculating your import VAT. A mistake here doesn't just cause a headache at the port; it can lead to incorrect VAT declarations and serious questions from the Federal Tax Authority (FTA). If you need a refresher, our guide on how to calculate VAT in the UAE walks through the specifics. Ultimately, precision with your HS code is your best defence against fines, shipment seizures, and supply chain chaos.
A Practical Workflow for Finding and Validating HS Codes
Working with the 12-digit HS code system day in and day out requires a solid, repeatable process. You simply can't afford to guess or blindly trust a supplier's paperwork—that’s a high-risk game that often ends in customs delays, fines, and a lot of headaches. A reliable workflow is your best defence, ensuring accuracy from the very beginning.
This process is built for the people on the ground—finance and logistics teams who need a clear path for finding, double-checking, and applying the right HS code Dubai Customs demands for every single shipment. Let's move past the theory and get into the practical steps you can use in your daily operations.
Starting With the Official Source: The Dubai Customs Portal
Your single source of truth is always the official Dubai Customs Tariff Code Search tool. Forget about third-party databases or that old spreadsheet someone saved years ago; they're often outdated and unreliable. Every search you conduct should start and end with this portal.
But it’s not as simple as just typing in a product name. To really nail down those final four digits of the code, you need to know your product inside and out. Vague descriptions like "computer parts" just won't cut it. You need to get specific.
- Material Composition: What’s it actually made of? Is it stainless steel, ABS plastic, or 100% cotton?
- Primary Function: What does it do? Is it for manufacturing another product, or is it a finished item for retail sale?
- Technical Specifications: What are its measurements, weight, power output, or other key technical details that set it apart?
Having these details ready before you even start your search will make the whole process faster and far more accurate.
Validating Supplier-Provided Codes
It's pretty standard for an overseas supplier to include an HS code on their commercial invoice. Think of this as a helpful suggestion, not the final word. You should never, ever accept it without doing your own homework.
Why? Because the supplier's code is usually only accurate for the first six digits—the part that’s harmonised globally. The rest of the code is specific to the GCC and the UAE, and as the importer of record, getting that part right is your responsibility. If it's wrong, the penalty falls on your business, not theirs.
Expert Tip: Create a simple dual-validation step in your process. When a supplier sends an HS code, use it as a starting point. Then, run your own classification search in the Dubai Customs portal. If you find a mismatch, dig into why and make sure you document your reasoning for the final code you choose.
This breakdown shows exactly why that local check is so important.
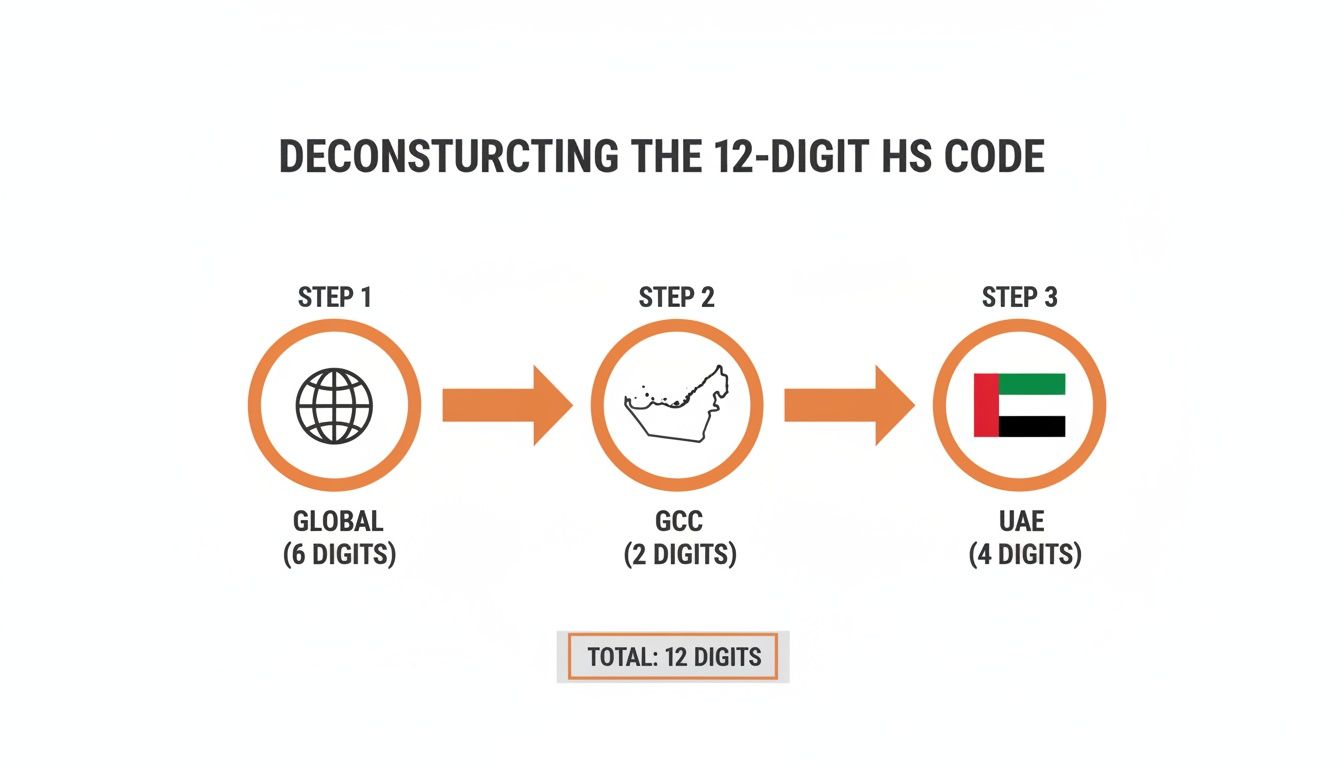
As you can see, half the code is determined locally. Relying only on an international supplier's information is a risk you don't need to take.
Real-World Classification Examples
Let's walk through how this works with a couple of common scenarios. The details are what make all the difference.
Scenario 1: Classifying Electronic Components Imagine you're importing microcontrollers to build smart home devices.
- Vague Description: "Electronic circuits"
- Detailed Description: "Mounted piezoelectric crystals, operating at a frequency of 20 MHz, for assembly into printed circuit boards."
- Classification Process: You'd start in Chapter 85 (Electrical machinery). From there, the detailed description allows you to zero in on the exact subheading for "mounted piezoelectric crystals" (8541.60). This level of detail is crucial for finding the correct UAE national code and distinguishing it from other types of integrated circuits.
Scenario 2: Classifying Food Items Now, let's say you're importing a shipment of organic coffee beans from Ethiopia.
- Vague Description: "Coffee"
- Detailed Description: "Unroasted, non-decaffeinated Arabica coffee beans, certified organic."
- Classification Process: Here, you'd begin in Chapter 09 (Coffee, Tea, Maté and Spices). The key details "unroasted" and "non-decaffeinated" point you directly to subheading 0901.11. The subsequent GCC and UAE-specific digits will likely factor in the bean type (Arabica) and organic certification, which can have a real impact on duties and inspection requirements.
When to Engage a Customs Broker
Even with a great internal process, there are times when you need to call in a specialist. For highly complex goods—think chemicals, pharmaceuticals, or sophisticated machinery—partnering with a licensed customs broker is a smart move.
A good broker lives and breathes the tariff schedule. They can help you get a binding ruling on a classification, giving you legal certainty. They're particularly valuable when a product could arguably fit into two different classifications with very different duty rates. It’s a similar logic to getting an expert for FTA TRN verification to ensure tax compliance; a broker provides that same level of assurance for customs. You can find out more about that in our guide on FTA TRN verification.
By building this clear, source-based workflow, you turn HS code classification from a guessing game into a controlled and compliant business process. That diligence is the key to avoiding costly mistakes and keeping your goods moving smoothly across UAE borders.
Avoiding Common HS Code Classification Mistakes
Getting an HS code wrong isn't just a simple typo. It's a compliance failure that can unleash a cascade of problems, from hefty financial penalties and frustrating shipment delays to having your goods seized by Dubai Customs. With the new 12-digit system now in place, you have to be more diligent than ever. Let’s walk through some of the most common pitfalls I see trip up even seasoned logistics teams.
One of the biggest sources of error right now is the hangover from the old system. So many businesses are still automatically pulling 8-digit codes from old invoices or internal master files. It's a habit, but it's a dangerous one. That old code is a direct path to getting your declaration rejected. What was perfectly acceptable last year is now a guaranteed headache at the border because the new system demands far more specific detail.
Another classic mistake is blindly trusting the HS code your supplier gives you. Sure, it’s a great starting point, but remember, their code is only truly reliable for the first six digits—that’s the part harmonised globally. As the official importer of record, your business is 100% responsible for getting the final six digits correct, which are specific to the GCC and the UAE. Just copying and pasting your supplier’s code is a shortcut that often leads to trouble.
Misinterpreting Product Details
This is where things can get tricky. One of the most nuanced errors is getting a product's primary function or material composition wrong. The HS code Dubai Customs uses is built on a very strict set of classification rules, and a product's intended purpose can completely change where it belongs. Think about a simple plastic component—is it part of a child's toy, a car, or an industrial machine? Each of those scenarios could land it in a completely different chapter.
This is exactly why detailed technical spec sheets are no longer a nice-to-have; they're essential. Vague descriptions are a recipe for ambiguous classifications. If you don't have precise information on what a product is made of, what it does, and even how it’s packaged for retail, you’re basically taking a guess. That kind of uncertainty is a major red flag for customs officials and makes it much more likely your shipment will be pulled for inspection.
An incorrect HS code classification is not just a logistical issue; it has direct financial consequences. It can lead to incorrect duty and VAT UAE calculations, resulting in underpayments that attract penalties from both Dubai Customs and the Federal Tax Authority (FTA).
To see how this plays out, imagine the difference between a standard office laptop and a ruggedised tablet built for a construction site. They're both computing devices, sure, but their unique features—like reinforced casings or specialised software—could easily place them in different national subheadings under the 12-digit system. And those different codes can have very different duty implications.
The Dangers of 'Tariff Engineering'
Now for a particularly risky manoeuvre: "tariff engineering." This is the practice of deliberately classifying a product under a code that has a lower duty rate to save money. While it might seem like a clever cost-cutting trick, Dubai Customs sees it as a serious compliance violation. Their systems are sophisticated and are designed to flag classifications that just don't seem right based on the product description or country of origin.
Getting caught doing this leads to consequences far worse than a simple fine. You could lose your trusted trader status and find every single one of your future shipments under a microscope. The short-term savings are never, ever worth the long-term damage to your company's reputation and its relationship with customs.
To make this clearer, I've put together a quick table that shows these common mistakes side-by-side with the best practices you should be following. It’s a straightforward guide to help you build a more accurate and defensible classification process.
Common HS Code Errors vs. Best Practices
| Common Mistake | Potential Consequence | Best Practice Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Using outdated 8-digit codes | Automatic declaration rejection, shipment delays, and storage fees. | Maintain a centralised, up-to-date HS code master file validated against the official Dubai Customs tariff schedule. |
| Blindly trusting supplier codes | Incorrect GCC/UAE digits, leading to wrong duty/VAT payments and fines. | Implement a dual-validation process: use the supplier's code as a reference but always conduct an independent classification. |
| Vague product descriptions | Ambiguous classification, increased inspections, and potential for misclassification penalties. | Develop detailed product specification sheets that include material composition, primary function, and technical details. |
| Engaging in 'tariff engineering' | Severe penalties, loss of customs privileges, and reputational damage. | Classify products based on their objective characteristics and intended use, consulting a customs broker for complex items. |
Ultimately, taking the time to get your HS codes right from the start saves you an enormous amount of time, money, and stress down the line. It's about building a robust process, not just finding a number that looks right.
Navigating the Transition Timeline and Action Items
Getting to grips with the new 12-digit HS code system is all about timing and preparation. Dubai Customs hasn't just flipped a switch overnight; they've structured a phased rollout that gives businesses a clear roadmap for getting their house in order. Think of this timeline not as a technicality, but as a critical project plan for your finance and logistics teams to ensure a smooth, penalty-free transition.
The shift to 12-digit HS codes is a multi-year process. During this window, you might find you can use both the old 8-digit and new 12-digit formats while your systems catch up. But don't get too comfortable. The GCC Integrated Customs Tariff is already live, meaning all UAE declarations must align with this wider regional framework.
As Deloitte has pointed out, getting the classification wrong under the GCC Common Customs Law can lead to some hefty fines. This is exactly why you need to be proactive—updating your internal item masters, getting new codes from suppliers, and briefing your customs broker well ahead of each deadline. You can read more from Deloitte on the UAE's expanded tariff code.

Understanding the Phased Rollout
Dubai Customs has been smart about this, designing an implementation timeline that prioritises different types of shipments to avoid a system-wide shock. The rollout strategically focuses on specific trade lanes and declaration types in distinct phases, which gives everyone a chance to adapt progressively.
Here’s a simplified breakdown of how these rollouts usually work:
- Phase 1: GCC Trade: Things usually kick off with shipments moving between Dubai and other GCC countries. Declarations like
IM4(Import to Local from GCC) are often the first to require the new 12-digit format. - Phase 2: Free Zones & Warehouses: Next, the focus typically shifts to goods moving from Free Zones and Customs Warehouses into the UAE mainland. This affects a huge volume of domestic trade that originates from these key hubs.
- Phase 3: Rest of World: This is the big one. This phase extends the 12-digit requirement to all mainland imports from non-GCC countries, covering the bulk of international trade.
- Phase 4: Temporary Operations: The final stage usually tidies up the more specialised declarations—think re-exports, temporary admissions for exhibitions, and other temporary goods movements.
Your Essential Action Plan
To stay ahead, your business needs a proactive strategy. Waiting until the last minute is a recipe for operational chaos and financial penalties. On the bright side, this transition is the perfect opportunity to align your customs data with other upcoming mandates, like the national UAE e-invoicing system. If you're looking into this, our comprehensive guide to UAE e-invoicing is a great place to start.
Here are the critical steps your team should be taking right now.
Audit Your Product Master Data
First things first: pull together a complete audit of your product master data. You need to identify every single product currently classified with an 8-digit HS code Dubai Customs previously accepted. This master list becomes the foundation of your update project. It’s a vital internal review that shows you the true scale of the task.
Update Suppliers and Customs Brokers
Get on the phone with your key suppliers and your customs broker. Let them know about your transition project and ask them to start providing the detailed product information you'll need to lock down the correct final four digits. Your broker, in particular, will be an invaluable partner in validating these new, more specific classifications.
Key Takeaway: The move to 12-digit HS codes isn't just an IT update; it's a fundamental change in process. It demands collaboration between finance, logistics, and procurement to get every product reclassified before the deadlines hit.
Upgrade Your Business Systems
Your ERP, accounting software, and any other platform that uses HS codes needs an update. This is more than just making a data field longer. You might need to adjust the logic within these systems to handle the new level of detail for reporting, duty calculations, and VAT assessment.
Train Your Finance and Logistics Teams
Finally, get your people trained. Your finance and logistics teams need to be completely comfortable with the new 12-digit structure and the internal workflows you've set up. Make sure they understand why this is happening, how to find and validate the new codes, and what the risks of non-compliance are. A well-informed team is your best defence against costly mistakes.
Getting Your Business Ready for Compliant Trade
Making the switch to the 12-digit HS code system that Dubai Customs now uses is a smart move. It’s all about creating more transparency and getting in line with global standards. Yes, it takes some effort upfront, but the payoff is huge: think smoother customs clearance, fewer financial risks, and much more accurate trade data. Getting this right sets your business up for efficient, hassle-free trading in the UAE’s dynamic economy.
Let's be clear: mastering the new 12-digit structure isn't just a good idea—it's essential. Your best defence against costly penalties is a solid internal process for checking and validating every code. Sticking to the official timeline means your supply chain won't hit any snags. By embracing these changes now, you're building a much stronger foundation for all your import and export operations.
How Customs Data Affects Your Wider Compliance
This update to HS codes doesn't happen in isolation. Your business is likely preparing for other big regulatory changes, like the UAE's upcoming e-invoicing mandate. This is a perfect time to ensure all your foundational data is clean and correct, as it's a crucial parallel task. An incorrect HS code, for instance, can throw off your duty and VAT UAE calculations on import declarations, leading to discrepancies that will cause headaches later on.
For finance managers and accountants, this really underscores the need for data integrity across the entire business. The details you handle for customs have a direct impact on your financial reporting and tax obligations. If you're looking to strengthen your overall FTA compliance, getting the fundamentals right is everything. Our guide on how to register for VAT in the UAE offers essential insights that fit perfectly with your customs compliance efforts.
The move to 12-digit HS codes is more than just a customs rule. It's a chance to seriously sharpen up your data management and get ready for a future where digital compliance—from customs declarations to the e-invoice—is standard practice.
Ultimately, being proactive is the only way to go. Audit your product master data now, get your teams trained on the new classification system, and you'll avoid that last-minute rush that always seems to lead to expensive mistakes. Ready to streamline your e-invoicing? Try Tadqiq today.